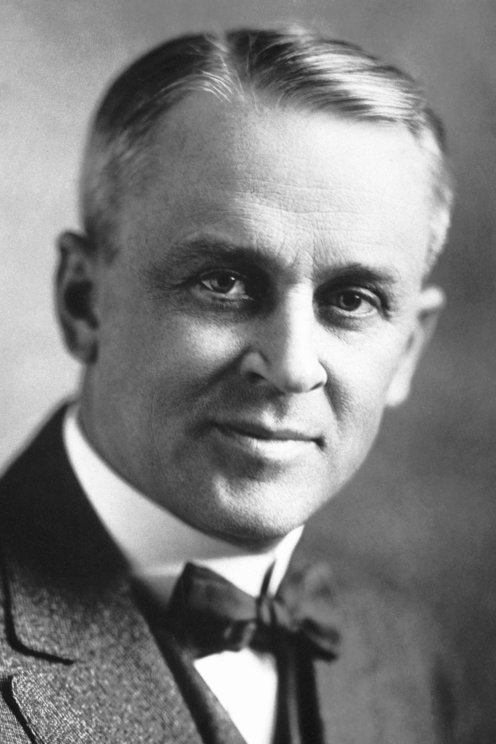| more general categories |
information about this item |
|
| 10. Noble Prize |
 |
 |
|
|
|
10. Noble Prize |
|
|
|
Physics (209) |
|
 |
| 11. Award Year |
 |
 |
|
|
|
11. Award Year |
|
|
|
1923 (5) |
|
 |
| 12. Winner Type |
 |
 |
|
|
|
12. Winner Type |
|
|
|
Person (904) |
|
 |
| 13. Gender |
 |
 |
|
|
|
13. Gender |
|
|
|
Male (853) |
|
 |
| 14. Birth Year |
 |
 |
|
|
|
14. Birth Year |
|
|
|
1868 (4) |
|
 |
| 15. Place of Birth |
 |
 |
|
|
|
15. Place of Birth |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Morrison (1) |
|
 |
| 16. Death Year |
 |
 |
|
|
|
16. Death Year |
|
|
|
1953 (3) |
|
 |
| 17. Place of Death |
 |
 |
|
|
|
17. Place of Death |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
San Marino (2) |
|
 |
| 19. Given Name |
 |
 |
|
|
|
19. Given Name |
|
|
|
R (80) |
|
 |
| 20. Family Name |
 |
 |
|
|
|
20. Family Name |
|
|
|
M (84) |
|
 |
| 21. Shared Given Name |
 |
 |
|
|
|
21. Shared Given Name |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Robert (29) |
|
 |
| 23. Religion |
 |
 |
|
|
|
23. Religion |
|
|
|
Christianity (158) |
|
 |
| 24. Age at Award Time |
 |
 |
|
|
|
24. Age at Award Time |
|
|
|
56 (23) |
|
 |
| 32. Occupations |
 |
 |
|
|
|
32. Occupations |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Physicists (206) |
|
 |
| 34. Citizens |
 |
 |
|
|
|
34. Citizens |
|
|
|
United States (307) |
|
 |
| 37. Worked for College or University |
 |
 |
|
|
|
37. Worked for College or University |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
California Institute of Technology (18) |
|
 |
| 42. Affilliation with College or University |
 |
 |
|
|
|
42. Affilliation with College or University |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Alumni (1) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Alumni (1) |
|
 |
| 44. Memberships |
 |
 |
|
|
|
44. Memberships |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Academy of Sciences of the USSR (80) |
|
|
|
American Academy of Arts and Sciences (531) |
|
|
|
American Association for the Advancement of Science (95) |
|
|
|
American Physical Society (113) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
French Academy of Sciences (89) |
|
|
|
German Academy of Sciences Leopoldina (179) |
|
|
|
Pontifical Academy of Sciences (83) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Russian Academy of Sciences (144) |
|
 |
| 45. Other Awards |
 |
 |
|
|
|
45. Other Awards |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
ASME Medal (1) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Comstock Prize in Physics (10) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Edison Medal (4) |
|
|
|
Faraday Lectureship Prize (22) |
|
|
|
Franklin Medal (45) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Hughes Medal (29) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Matteucci Medal (29) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Oersted Medal (8) |
|
 |
| complete name: |
Robert Millikan |
| nobel prize: |
physics |
| award year: |
1923 |
| prize share: |
Prize share: 1/1 |
| rational: |
The Nobel Prize in Physics 1923 was awarded to Robert Andrews Millikan "for his work on the elementary charge of electricity and on the photoelectric effect." |
| biography: |
Biography |
| laureate facts: |
Facts |
| laureate lecture: |
Lecture |
| given name: |
Robert |
| family name: |
Millikan |
| occupation: |
physicist |
| occupation: |
university teacher |
| field of work: |
physics |
| work location: |
University of Chicago, 5801 S Ellis Ave, Chicago, IL, 60637, United States of America |
| description: |
Robert Millikan was an American experimental physicist honored with the Nobel Prize for Physics in 1923 for his measurement of the elementary electronic charge and for his work on the photoelectric effect. Millikan graduated from Oberlin College in 1891 and obtained his doctorate at Columbia University in 1895. In 1896 he became an assistant at the University of Chicago, where he became a full professor in 1910. In 1909 Millikan began a series of experiments to determine the electric charge carried by a single electron. He began by measuring the course of charged water droplets in an electric field. The results suggested that the charge on the droplets is a multiple of the elementary electric charge, but the experiment was not accurate enough to be convincing. He obtained more precise results in 1910 with his famous oil-drop experiment in which he replaced water (which tended to evaporate too quickly) with oil. In 1914 Millikan took up with similar skill the experimental verification of the equation introduced by Albert Einstein in 1905 to describe the photoelectric effect. He used this same research to obtain an accurate value of Planck’s constant. In 1921 Millikan left the University of Chicago to become director of the Norman Bridge Laboratory of Physics at the California Institute of Technology (Caltech) in Pasadena, California. There he undertook a major study of the radiation that the physicist Victor Hess had detected coming from outer space. Millikan proved that this radiation is indeed of extraterrestrial origin, and he named it "cosmic rays." As chairman of the Executive Council of Caltech (the school's governing body at the time) from 1921 until his retirement in 1945, Millikan helped to turn the school into one of the leading research institutions in the United States. He also served on the board of trustees for Science Service, now known as Society for Science & the Public, from 1921 to 1953. |
| image copyright: |
Photo from the Nobel Foundation archive. |
| image citation: |
The Nobel Prize in Physics 1923. NobelPrize.org. Nobel Media AB 2018. <https://www.nobelprize.org/prizes/physics/1923/summary/> |
| date birth: |
1868 |
| date death: |
1953 |
| usual name: |
Robert Millikan |